Scientific Gateway for HPC
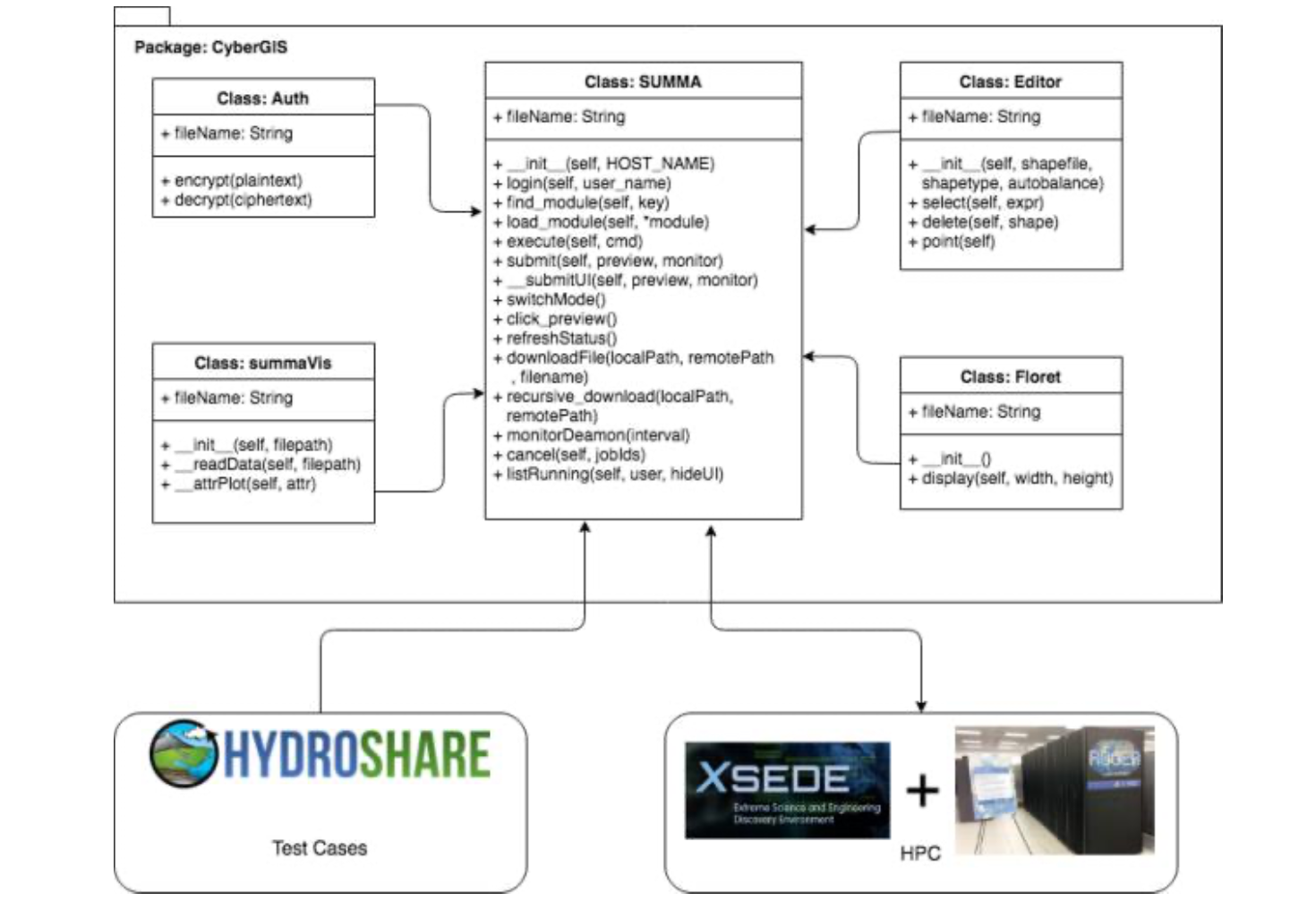
Scientific Gateway for Hydrological SUMMA Model
Lyu, F., Yin, D., Padmanabhan, A., Choi, Y., Goodall, J., Castronova, A, Tarboton, D., Wang, S. (2019). Reproducible Hydrolog‑ ical Modeling with CyberGIS‑Jupyter: A Case Study on SUMMA. In: Proceedings of Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing (PEARC19), Chicago, Illinois, USA, July 28 – August 1, 2019. DOI: 10.1145/3332186.3333052
CyberGIS-Jupyter is a cyberGIS framework for achieving data-intensive, reproducible, and scalable geospatial analytics using Jupyter Notebook based on advanced cyberinfrastructure. As a cutting-edge hydrological modeling framework, the Structure for Unifying Multiple Modeling Alternative (SUMMA) functions as a unified approach to process-based modeling. The purpose of this research is to investigate the feasibility of coupling CyberGIS-Jupyter with SUMMA to realize reproducible hydrological modeling. CyberGIS-Jupyter is employed to systematically integrate advanced cyberinfrastructure, including two high-performance computers – Virtual ROGER and XSEDE Comet, data management, and execution and visualization of SUMMA-based modeling. By taking advantage of CyberGIS-Jupyter, users can easily tune different parameters for a SUMMA model and submit computational jobs for executing the model on HPC resources without having to possess in-depth technical knowledge about cyberGIS or cyberinfrastructure. Computational experiments demonstrate that the integration of CyberGIS-Jupyter and SUMMA achieves a high-performance and easy-to-use implementation for reproducible SUMMA-based hydrological modeling.
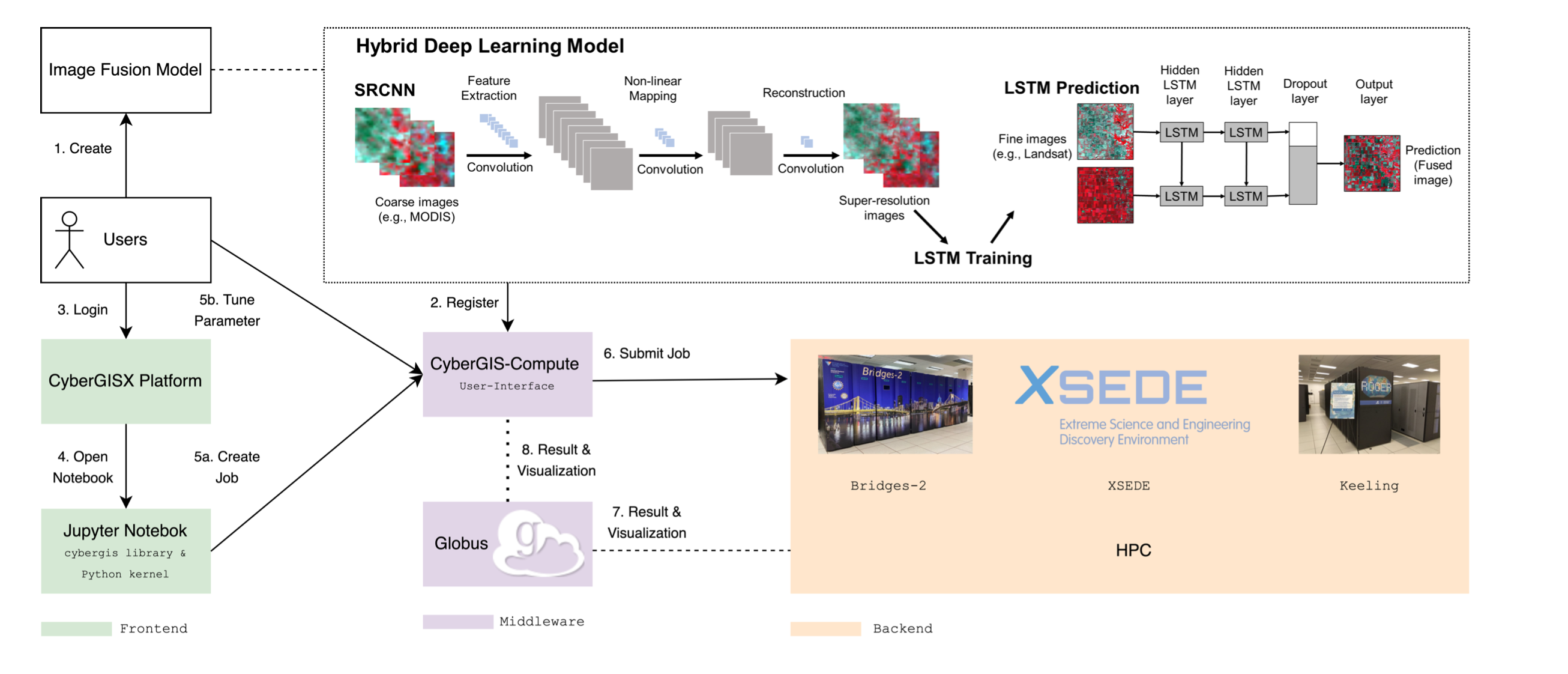
Scientific Gateway for Remote Sensing Image Fusion Model
Lyu, F., Yang, Z., Xiao, Z., Diao, C., Park, J., Wang, S. (2022). CyberGIS for Scalable Remote Sensing Data Fusion. In: Proceed‑ ings of Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing (PEARC22), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 35, 1–4. DOI: 10.1145/3491418.3535145
Satellite remote sensing data products are widely used in many applications and science domains ranging from agriculture and emergency management to Earth and environmental sciences. Researchers have developed sophisticated and computationally intensive models for processing and analyzing such data with varying spatiotemporal resolutions from multiple sources. However, the computational intensity and expertise in using advanced cyberinfrastructure have held back the scalability and reproducibility of such models. To tackle this challenge, this research employs the CyberGIS-Compute middleware to achieve scalable and reproducible remote sensing data fusion across multiple spatiotemporal resolutions by harnessing advanced cyberinfrastructure. CyberGIS-Compute is a cyberGIS middleware framework for conducting computationally intensive geospatial analytics with advanced cyberinfrastructure resources such as those provisioned by XSEDE. Our case study achieved remote sensing data fusion at high spatial and temporal resolutions based on integrating CyberGIS-Compute with a cutting-edge deep learning model. This integrated approach also demonstrates how to achieve computational reproducibility of scalable remote sensing data fusion.